Arthritis is the most common cause of knee pain. Knee Arthritis is a condition where the bones rub against each other due to wear and tear of the supportive cartilage within the knee joint.
The most common causes of arthritis are Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Traumatic arthritis and Gout.
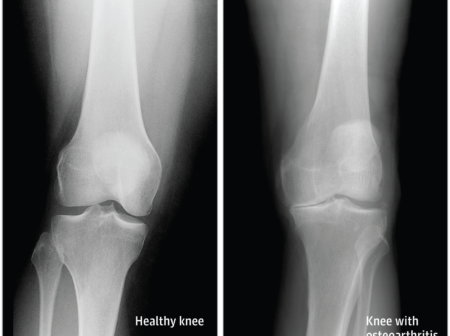
Osteoarthritis
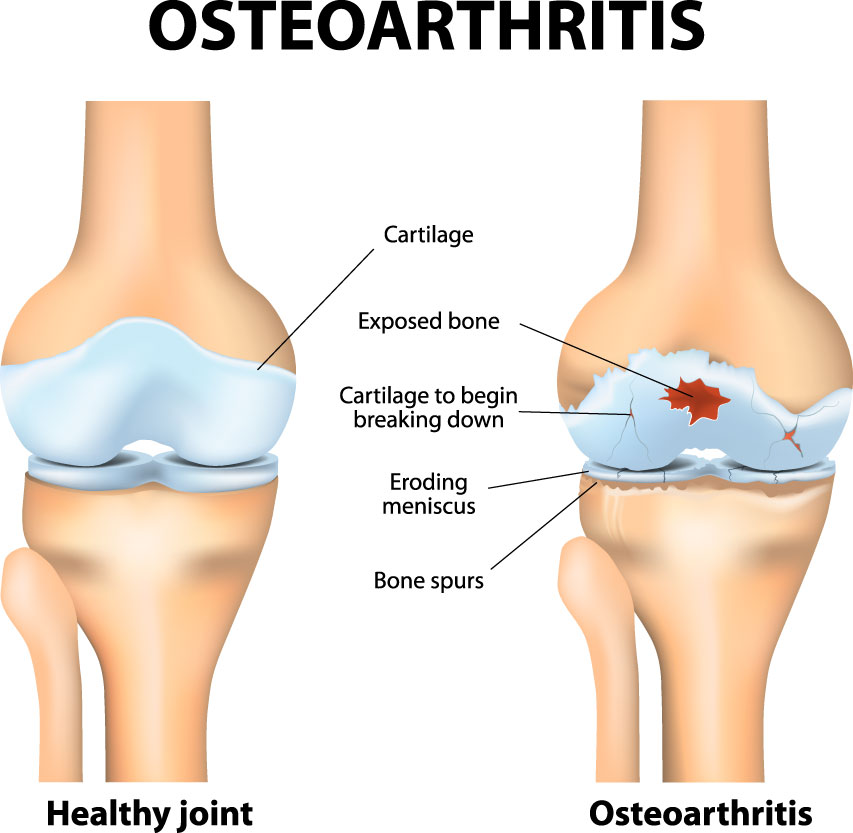 Osteoarthritis usually starts after the age of 40. It is a progressive condition which causes the degeneration of the cartilage within the knee joint. The cartilage acts as a cushion between the two major bones in the leg. Due to osteoarthritis, the cartilage wears away leading to two bones rubbing against each other and cause pain and restriction of movement.
Osteoarthritis usually starts after the age of 40. It is a progressive condition which causes the degeneration of the cartilage within the knee joint. The cartilage acts as a cushion between the two major bones in the leg. Due to osteoarthritis, the cartilage wears away leading to two bones rubbing against each other and cause pain and restriction of movement.
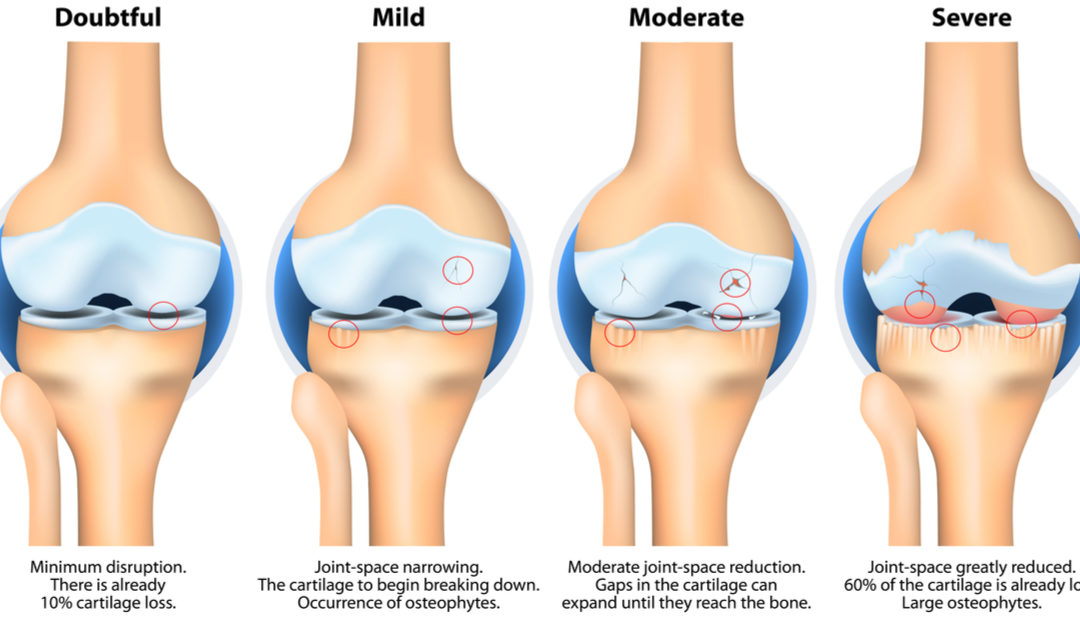
This pain usually starts with a low-intensity pain which keeps on increasing. During the later age, it can become so severe that it interferes with daily activities and disturbs sleep. There can also be a swelling or stiffening of the knee joint leading to decreased movement.
In the early stages, the condition can be managed in various ways:
- Weight loss
- Physiotherapy
- Standard Joint Preserving Exercises
- Intra Joint Injection
- Medicine (Non-Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs and steroids)
The absolute treatment is a Half or Total Knee Replacement surgery.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory condition of the lining of the Knee Joint, namely the Synovium/Joint capsule.
It is believed to be caused by self-attacking antibodies produced by one’s own body. A genetic cause has also been thought of for the same. This starts much earlier in life commonly around the age of 20 to 30 years.
Along with the normal symptoms of arthritis namely, pain, swelling and stiffness, Rheumatoid arthritis generally affects more than one joint at the same time. Rheumatoid Arthritis can also be associated with many other conditions throughout the body, like skin nodules, nerves entrapment, muscle pains and other vital organ involvement.
A treatment plan has to be worked out with your Doctor to help achieve the best quality of life possible and Total Knee Replacement surgery could be very beneficial to the patients who have a severe disability due to Rheumatoid Arthritis of the knee.
Traumatic Arthritis
A condition which follows an injury to the joint in the form of a Fracture or ligament tear around the knee joint.
Even though a knee injury may heal it may cause the joint to move differently due to a ligament injury and cause more wear on the cartilage and knees. When this happens, the prior injury often resurfaces in the form of post-traumatic knee arthritis after a few decades.
The patients generally suffer from the following symptoms of post-traumatic knee arthritis.
- Joint swelling
- Joint redness and warmth
- Knee pain, especially when weight is applied
- Stiffness
- A “crunching” sensation when moving the knee joint
- Weakness or buckling in the knee (due to ligament tear)
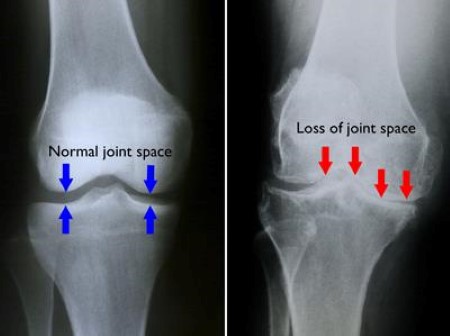
The doctor diagnoses the condition by a proper physical examination of the knee joint. Relevant blood tests and X rays are done.
Sometimes it may be necessary to perform a CT scan or MRI scan to understand the severity of the injury.
Treatment for post-traumatic knee arthritis depends upon the severity of the condition. Treatment can also help prevent further damage to the knee joint.
Treatment options are below:
- Rest
- Physical therapy
- Exercise (low impact)
- Knee Injections
- Medication supervised by a doctor
- Weight loss
If conservative treatments fail to improve knee function and discomfort, one may be a candidate for a surgical treatment.
The surgery options are below:
- Arthroscopy and Meniscal or Ligament Surgery
- Alignment Osteotomy (for bent legs)
- Partial Knee Replacement
- Total Knee Replacement
Treatments Offered